Which Layer Of The Osi Model Adds Source And Destination Mac Addresses To Frames?
What is OSI Model?
The OSI Model is a logical and conceptual model that defines network communication used by systems open up to interconnection and communication with other systems. The Open up System Interconnection (OSI Model) besides defines a logical network and finer describes computer packet transfer by using various layers of protocols.
In this tutorial, you lot will larn:
- Characteristics of OSI Model
- Why of OSI Model?
- What is OSI Model?
- History of OSI Model
- 7 Layers of the OSI Model
- Physical Layer
- Data Link Layer
- Ship Layer
- Network Layer
- Session Layer
- Presentation Layer
- Application Layer
- Interaction Between OSI Model Layers
- Protocols supported at various levels
- Differences betwixt OSI & TCP/IP
- Advantages of the OSI Model
- Disadvantages of the OSI Model
Characteristics of OSI Model
Here are some important characteristics of the OSI model:
- A layer should only be created where the definite levels of abstraction are needed.
- The function of each layer should be selected as per the internationally standardized protocols.
- The number of layers should exist large so that separate functions should not be put in the same layer. At the same fourth dimension, it should exist small enough so that architecture doesn't become very complicated.
- In the OSI model, each layer relies on the side by side lower layer to perform primitive functions. Every level should able to provide services to the next higher layer
- Changes made in one layer should not need changes in other lavers.
Why of OSI Model?
- Helps you to understand advice over a network
- Troubleshooting is easier by separating functions into different network layers.
- Helps you lot to empathise new technologies as they are developed.
- Allows you lot to compare primary functional relationships on various network layers.
History of OSI Model
Here are essential landmarks from the history of OSI model:
- In the belatedly 1970s, the ISO conducted a program to develop general standards and methods of networking.
- In 1973, an Experimental Parcel Switched Organisation in the Great britain identified the requirement for defining the higher-level protocols.
- In the yr 1983, OSI model was initially intended to be a detailed specification of actual interfaces.
- In 1984, the OSI compages was formally adopted by ISO equally an international standard
vii Layers of the OSI Model
OSI model is a layered server architecture system in which each layer is defined according to a specific office to perform. All these seven layers work collaboratively to transmit the data from one layer to another.
- The Upper Layers: It deals with application issues and mostly implemented simply in software. The highest is closest to the end system user. In this layer, communication from one end-user to another begins past using the interaction between the application layer. It will process all the mode to end-user.
- The Lower Layers: These layers handle activities related to data transport. The physical layer and datalink layers too implemented in software and hardware.
Upper and Lower layers further divide network architecture into 7 different layers every bit below
- Awarding
- Presentation
- Session
- Transport
- Network, Data-link
- Physical layers
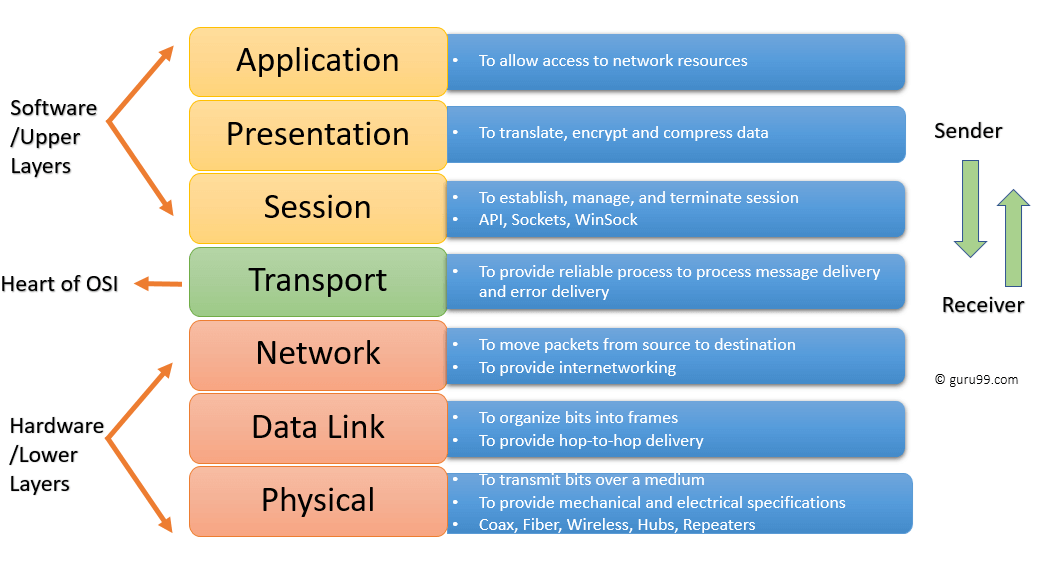
Let'southward Study each layer in particular:
Physical Layer
The physical layer helps you to define the electrical and physical specifications of the data connection. This level establishes the relationship between a device and a physical transmission medium. The physical layer is not concerned with protocols or other such higher-layer items.
Examples of hardware in the physical layer are network adapters, ethernet, repeaters, networking hubs, etc.
Information Link Layer:
Information link layer corrects errors which can occur at the physical layer. The layer allows yous to define the protocol to establish and terminates a connection between 2 continued network devices.
It is IP accost understandable layer, which helps you to define logical addressing so that whatever endpoint should exist identified.
The layer also helps you implement routing of packets through a network. It helps you to define the all-time path, which allows y'all to take data from the source to the destination.
The data link layer is subdivided into 2 types of sublayers:
- Media Access Control (MAC) layer- It is responsible for controlling how device in a network gain access to medium and permits to transmit data.
- Logical link command layer- This layer is responsible for identity and encapsulating network-layer protocols and allows you to discover the error.
Important Functions of Datalink Layer:
- Framing which divides the data from Network layer into frames.
- Allows yous to add header to the frame to define the physical address of the source and the destination machine
- Adds Logical addresses of the sender and receivers
- It is too responsible for the sourcing process to the destination process delivery of the entire message.
- Information technology likewise offers a organization for error control in which it detects retransmits damage or lost frames.
- Datalink layer also provides a mechanism to transmit data over independent networks which are linked together.
Transport Layer:
The ship layer builds on the network layer to provide data send from a process on a source machine to a process on a destination machine. It is hosted using single or multiple networks, and too maintains the quality of service functions.
Information technology determines how much data should be sent where and at what rate. This layer builds on the message which are received from the application layer. It helps ensure that information units are delivered error-complimentary and in sequence.
Ship layer helps you to control the reliability of a link through flow command, error control, and sectionalization or desegmentation.
The transport layer also offers an acknowledgment of the successful data transmission and sends the side by side information in example no errors occurred. TCP is the best-known example of the transport layer.
Important functions of Transport Layers:
- It divides the bulletin received from the session layer into segments and numbers them to brand a sequence.
- Transport layer makes sure that the message is delivered to the correct process on the destination machine.
- It also makes sure that the unabridged bulletin arrives without any error else it should exist retransmitted.
Network Layer:
The network layer provides the functional and procedural means of transferring variable length data sequences from i node to another connected in "dissimilar networks".
Message delivery at the network layer does not give whatever guaranteed to exist reliable network layer protocol.
Layer-direction protocols that belong to the network layer are:
- routing protocols
- multicast grouping direction
- network-layer address assignment.
Session Layer
Session Layer controls the dialogues between computers. It helps you to establish starting and terminating the connections between the local and remote application.
This layer request for a logical connection which should be established on end user'south requirement. This layer handles all the important log-on or countersign validation.
Session layer offers services like dialog subject field, which tin exist duplex or half-duplex. It is by and large implemented in application environments that use remote process calls.
Important function of Session Layer:
- Information technology establishes, maintains, and ends a session.
- Session layer enables two systems to enter into a dialog
- It also allows a process to add together a checkpoint to steam of data.
Presentation Layer
Presentation layer allows yous to define the course in which the data is to exchange between the two communicating entities. It also helps you to handles data compression and data encryption.
This layer transforms information into the class which is accepted by the awarding. It also formats and encrypts data which should be sent across all the networks. This layer is likewise known equally a syntax layer.
The role of Presentation Layers:
- Character code translation from ASCII to EBCDIC.
- Data pinch: Allows to reduce the number of bits that needs to be transmitted on the network.
- Data encryption: Helps yous to encrypt data for security purposes — for example, password encryption.
- It provides a user interface and support for services like e-mail and file transfer.
Awarding Layer
Awarding layer interacts with an application program, which is the highest level of OSI model. The awarding layer is the OSI layer, which is closest to the cease-user. It ways OSI application layer allows users to collaborate with other software application.
Application layer interacts with software applications to implement a communicating component. The interpretation of information by the application program is ever outside the telescopic of the OSI model.
Example of the application layer is an application such as file transfer, electronic mail, remote login, etc.
The function of the Awarding Layers are:
- Application-layer helps you to identify communication partners, determining resource availability, and synchronizing communication.
- It allows users to log on to a remote host
- This layer provides various e-mail services
- This application offers distributed database sources and access for global information nigh various objects and services.
Interaction Between OSI Model Layers
Information sent from a one computer application to another needs to pass through each of the OSI layers.
This is explained in the below-given example:
- Every layer within an OSI model communicates with the other two layers which are below it and its peer layer in some some other networked computing organization.
- In the below-given diagram, you lot can come across that the data link layer of the first system communicates with two layers, the network layer and the physical layer of the arrangement. Information technology also helps y'all to communicate with the data link layer of, the 2nd system.

Protocols supported at various levels
| Layer | Name | Protocols |
|---|---|---|
| Layer vii | Application | SMTP, HTTP, FTP, POP3, SNMP |
| Layer 6 | Presentation | MPEG, ASCH, SSL, TLS |
| Layer 5 | Session | NetBIOS, SAP |
| Layer 4 | Transport | TCP, UDP |
| Layer 3 | Network | IPV5, IPV6, ICMP, IPSEC, ARP, MPLS. |
| Layer ii | Information Link | RAPA, PPP, Frame Relay, ATM, Fiber Cable, etc. |
| Layer 1 | Physical | RS232, 100BaseTX, ISDN, 11. |
Differences between OSI & TCP/IP

Hither, are some of import differences betwixt the OSI & TCP/IP model:
| OSI Model | TCP/IP model |
|---|---|
| OSI model provides a clear stardom betwixt interfaces, services, and protocols. | TCP/IP doesn't offering whatever clear distinguishing points betwixt services, interfaces, and protocols. |
| OSI uses the network layer to define routing standards and protocols. | TCP/IP uses only the Internet layer. |
| OSI model utilize 2 divide layers concrete and information link to define the functionality of the bottom layers | TCP/IP uses only one layer (link). |
| OSI model, the send layer is only connection-oriented. | A layer of the TCP/IP model is both connection-oriented and connectionless. |
| In OSI model, data link layer and physical are separate layers. | In TCP information link layer and physical layer are combined as a unmarried host-to-network layer. |
| The minimum size of the OSI header is five bytes. | Minimum header size is 20 bytes. |
Advantages of the OSI Model
Hither, are major benefits/pros of using the OSI model :
- Information technology helps y'all to standardize router, switch, motherboard, and other hardware
- Reduces complexity and standardizes interfaces
- Facilitates modular engineering science
- Helps yous to ensure interoperable engineering
- Helps you to advance the evolution
- Protocols can be replaced past new protocols when technology changes.
- Provide support for connection-oriented services also as connectionless service.
- Information technology is a standard model in calculator networking.
- Supports connectionless and connection-oriented services.
- Offers flexibility to adapt to diverse types of protocols
Disadvantages of the OSI Model
Here are some cons/ drawbacks of using OSI Model:
- Plumbing equipment of protocols is a ho-hum task.
- Yous can but use it as a reference model.
- Doesn't define any specific protocol.
- In the OSI network layer model, some services are duplicated in many layers such as the transport and data link layers
- Layers can't piece of work in parallel every bit each layer need to wait to obtain data from the previous layer.
Summary
- The OSI Model is a logical and conceptual model that defines network communication which is used past systems open to interconnection and communication with other systems
- In OSI model, layer should simply be created where the definite levels of brainchild are needed.
- OSI layer helps you lot to empathise communication over a network
- In 1984, the OSI architecture was formally adopted by ISO as an international standard
| Layer | Proper name | Function | Protocols |
|---|---|---|---|
| Layer 7 | Application | To let access to network resources. | SMTP, HTTP, FTP, POP3, SNMP |
| Layer 6 | Presentation | To interpret, encrypt and compress data. | MPEG, ASCH, SSL, TLS |
| Layer 5 | Session | To establish, manage, and terminate the session | NetBIOS, SAP |
| Layer 4 | Ship | The transport layer builds on the network layer to provide data transport from a process on a source machine to a process on a destination machine. | TCP, UDP |
| Layer three | Network | To provide internetworking. To move packets from source to destination | IPV5, IPV6, ICMP, IPSEC, ARP, MPLS. |
| Layer 2 | Information Link | To organize $.25 into frames. To provide hop-to-hop commitment | RAPA, PPP, Frame Relay, ATM, Cobweb Cable, etc. |
| Layer i | Physical | To transmit bits over a medium. To provide mechanical and electrical specifications | RS232, 100BaseTX, ISDN, eleven. |
Which Layer Of The Osi Model Adds Source And Destination Mac Addresses To Frames?,
Source: https://www.guru99.com/layers-of-osi-model.html
Posted by: ackermanpubleausing1955.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Which Layer Of The Osi Model Adds Source And Destination Mac Addresses To Frames?"
Post a Comment