
Angular Acceleration and Moment of Inertia in Car Pattern
As a provider of flexible drive couplings and brawl detent safety clutches, we are often asked to provide a bit of aid in computing application torques, especially for customers looking to retrofit existing equipment. In society to aid in the procedure of estimating torques, we'll review one of the basic calculations used to estimate the torque required to accelerate a rotating mass to a certain speed over a given time.
Athwart dispatch (α) tin can be divers equally athwart velocity (ω) divided by acceleration time (t). Alternatively, pi (π) multiplied by drive speed (n) divided by acceleration time (t) multiplied by 30. This equation yields the standard athwart dispatch SI unit of radians per second squared (Rad/sec^ii). The equation below defines the rate of alter of angular velocity.
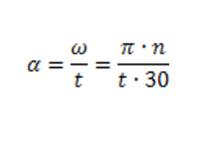
ω = angular velocity in the standard SI unit of radians per second (Rad/sec), 1 radian = 57.3 degrees
t = acceleration time in seconds
π = three.1416
n = drive speed in revolutions per minute RPM
In the adjacent example, angular velocity will be calculated for acceleration from 0 to 60 RPM in one 2nd. Annotation that 2π radians per second = 60 RPM.
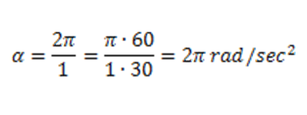
This adding is very useful in auto design considering angular acceleration multiplied past rotational moment of inertia equals torque. Keep in mind that the verbal moment of inertia tin can be difficult to calculate based on complex geometries in real drive lines, and other variables such equally friction are not considered in the next calculation. Nonetheless it is still very helpful in approximating torque requirements or establishing baseline minimum values for component sizing purposes.

J = moment of inertia in kg∙yard2
T= torque in N∙m
N= force in Newtons
kg= mass in kilograms
m= lever arm radius in meters
In the final example below nosotros will use the angular acceleration we plant above to calculate torque on a flywheel with a 1 meter radius and m kg mass.
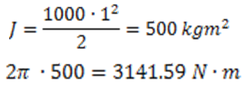
Every bit we can come across, if a flywheel with a 1 meter radius and chiliad kg mass were to be accelerated to 60 RPM in one second, it would crave 3141.59 Newton meters of input torque.
I hope you institute this refresher on calculating athwart acceleration to be helpful. If you have questions pertinent to the sizing and application of shaft couplings or safety clutches, experience gratis to contact our applications engineering section.
applications@rw-america.com



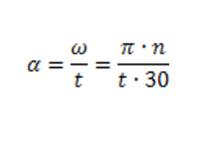
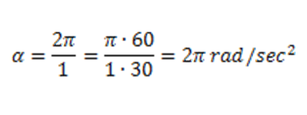

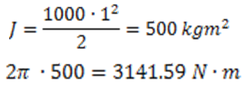

0 Response to "Angular Acceleration Of A Cylinder"
Post a Comment