How To Add A Byte To The End Of A Byte Array
Many unlike types of data objects are supported past Python. 2 of them are the objects bytearray and bytes. The bytearray() office returns an array object of bytes. This object is changeable and supports the integer number from 0 to 255. The bytes() function returns bytes objects, is not changeable, and supports the integers from 0 to 255. This article will describe these functions and explain how bytearray objects can be converted into bytes objects.
Syntax of bytearray() Method
bytearray ( [ data_source [ , encoding [ , errors] ] ] )
The three arguments of this method are optional. The kickoff argument is used to initialize the listing of bytes. If the start argument is the string, then the 2nd argument is used for encoding. Finally, the third argument is used to display the error if the encoding fails.
Syntax of bytes() Method
bytes ( [data_source [ , encoding [ , errors] ] ] )
All arguments of the bytes() function are optional, like the bytearray() method. The functions of these arguments are as well the same every bit the bytearray() method, mentioned in a higher place.
The method for converting bytearray to bytes in Python is shown beneath, using some unproblematic examples for meliorate understanding of this process.
Example 1: Convert Listing Data from bytearray to bytes
When the bytearray() part contains only 1 argument, the value of the argument will exist a dictionary datum or variable. The following example shows how a lexicon object can be converted into a bytearray object and how a bytearray object can and so be converted into a byte object. Next, the offset for loop is used to display the values of the translation table of ASCII codes and the second for loop is used to display the characters of the corresponding ASCII codes.
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# Ascertain the list
listdata = [ 72 , 69 , 76 , 76 , 79 ]
# Print the content of the list
print ( "\nThe dictionary values are :\n" , listdata)
# Initialize bytearray object with listing
byteArrayObject = bytearray (listdata)
# Print bytearray object value
print ( "\nThe output of bytearray() method :\due north" , byteArrayObject)
# Convert the bytearray object into bytes object
byteObject = bytes (byteArrayObject)
# Impress bytes object value
print ( "\nThe output of bytes() method :\n" , byteObject)
print ( "\northThe ASCII values of bytes" )
# Iterate the bytes object using loop
for val in byteObject:
print (val, ' ' , end= '' )
print ( "\nThe string values of bytes" )
# Iterate the bytes object using loop
for val in byteObject:
print ( chr (val) , ' ' , end= '' )
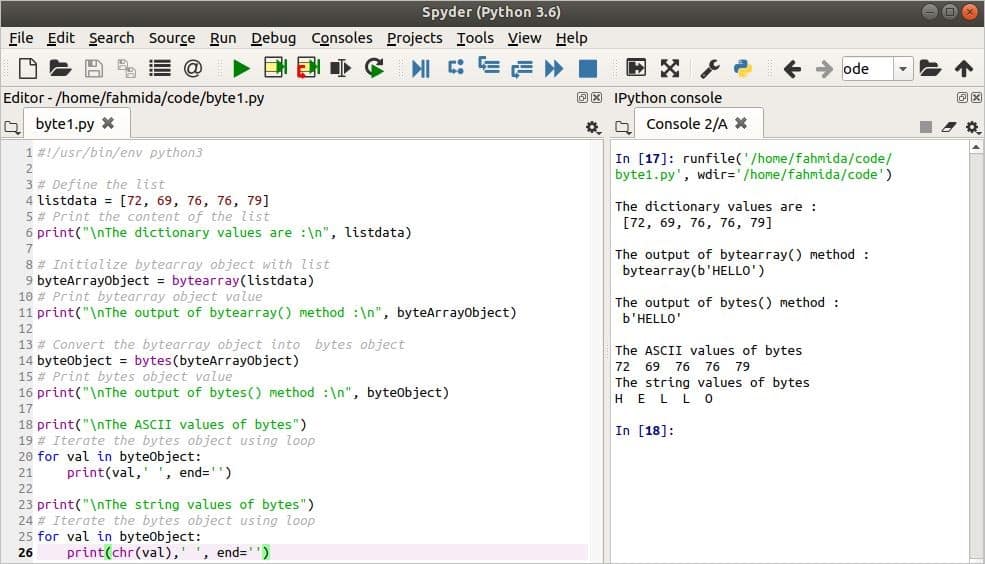
Output
The following output will announced after running the script. Here, 72, 69, 76, and 79 are the ASCII code of 'H,' 'E,' '50,' and 'O,' respectively.
Example two: Convert String Data from bytearray to bytes
The post-obit example shows the conversion of bytearray objects to byte objects in string data. 2 arguments are used in the bytearray() method of this script. The offset statement contains the string value, while the second argument contains the encoding string. Here, 'utf-8' encoding is used to convert into a bytearray object. The decode() method is used in the script to convert the bytes objects into string information. The same encoding is used at the time of conversion.
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# Have a cord value
text = input ( "Enter any text:\north" )
# Initialize bytearray object with string and encoding
byteArrObj = bytearray (text, 'utf-8' )
print ( "\nThe output of bytesarray() method :\northward" , byteArrObj)
# Catechumen bytearray to bytes
byteObj = bytes (byteArrObj)
impress ( "\nThe output of bytes() method :\northward" , byteObj)
# Convert bytes value into string using emcoding
print ( "\northwardThe string values of bytes" )
print (byteObj.decode ( "utf-8" ) )
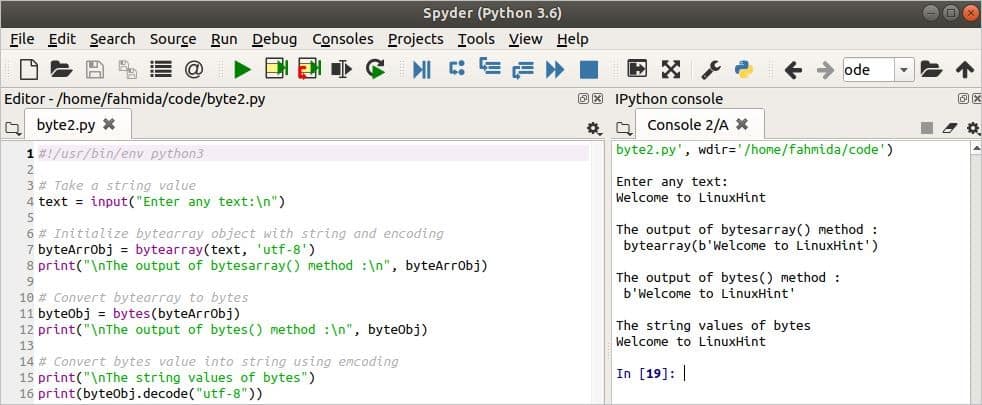
Output
The following output volition appear later on running the script.
Instance iii: Convert Integer Information from bytearray to bytes
The previous examples show the conversion of bytearray and bytes based on lexicon and cord data. This third example shows the conversion of bytearray into bytes based on the input information. Here, the input value is converted into an integer value and passed every bit an argument via the bytearray() function, and the bytearray object is then converted into a bytes object. The zero values based on the integer number are shown as an output of the bytearray and bytes object. The total number of bytes is counted via the len() method at the end of the script, and volition be equal to the integer value passed as an argument into the bytearray() method.
#!/usr/bin/env python3
effort:
# Have whatever number value
text = int ( input ( "Enter any number: " ) )
# Initialize bytearray object with number
byteArrObj = bytearray (text)
print ( "\nThe output of bytesarray() method :\n" , byteArrObj)
# Convert bytearray object to bytes object
byteObj = bytes (byteArrObj)
print ( "\due northThe output of bytes() method :\n" , byteObj)
# Impress the size of the bytes object
print ( "\nThe lenght of the bytes object: " , len (byteObj) )
except ValueError:
print ( "Enter whatever numeric value" )
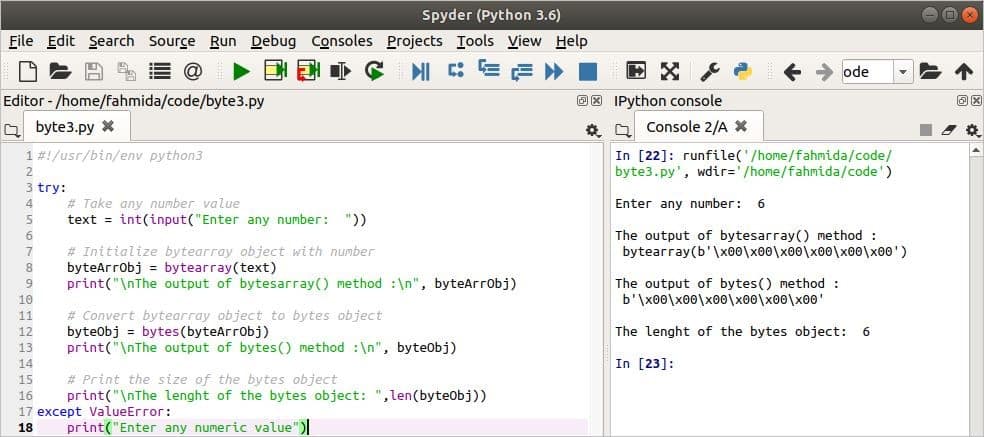
Output
After running the script, vi is taken as input in the following output. The vi null values are displayed as the output of bytearray and bytes. When the naught values are counted then it displayed vi.
Case 4: Create bytearray Using append() and Convert to bytes
The following example shows how bytearray objects can exist created via the append() method and converted into bytes. The arrVal variable is declared here as a bytearray object. Next, the append() method is called six times to add six elements into the array. The ASCII codes of the characters, 'P,' 'y,' 't,' 'h,' 'o,' and 'due north,' are eighty, 121, 116, 104, 111 and 1120, respectively. These are added in the bytearray object. This array object is converted into the bytes object after.
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# Create bytearray and add detail using append() method
arrVal = bytearray ( )
arrVal.suspend ( 80 )
arrVal.append ( 121 )
arrVal.append ( 116 )
arrVal.append ( 104 )
arrVal.suspend ( 111 )
arrVal.append ( 110 )
# Print the bytearray() values
print ( "\nThe output of bytearray() method :\north" , arrVal)
# Catechumen the bytearray object into a bytes object
byteObject = bytes (arrVal)
# Impress bytes object value
print ( "\nThe output of bytes() method :\n" , byteObject)
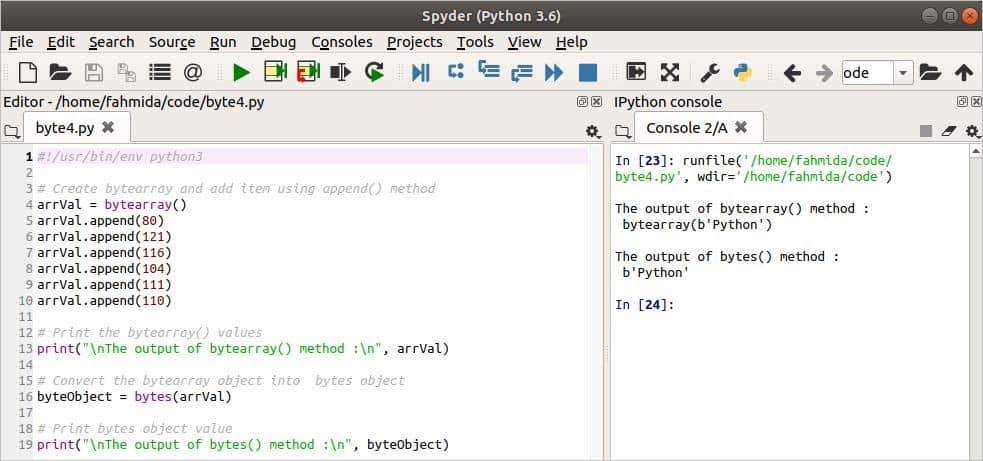
Output
The post-obit output will appear afterwards running the script.
Determination
Diverse methods are shown in this article for converting bytearray to bytes afterwards creating bytearray objects. Afterwards reading this article, I hope that you understand the concept of bytearray and bytes, know the way to convert bytearray to bytes, and exist able to brandish the output of bytes equally string and characters.
How To Add A Byte To The End Of A Byte Array,
Source: https://linuxhint.com/convert_bytearray_bytes_python/
Posted by: ackermanpubleausing1955.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Add A Byte To The End Of A Byte Array"
Post a Comment